Purpose
A Wonderful Relations Form is a structured way to collect and manage data. Unlike traditional form builders that store data as meta values, a Wonderful Relations Form directly maps form fields to a database table or to WordPress options (wp_options). This ensures structured storage, better performance, and seamless integration with other database-driven applications.
Forms in Wonderful Relations standardize both input handling and design while remaining flexible. Each form includes fields, buttons, linked forms, tasks, and options, allowing for automation, validation, and extended functionality.
Visual Example
Backend:
Parameters
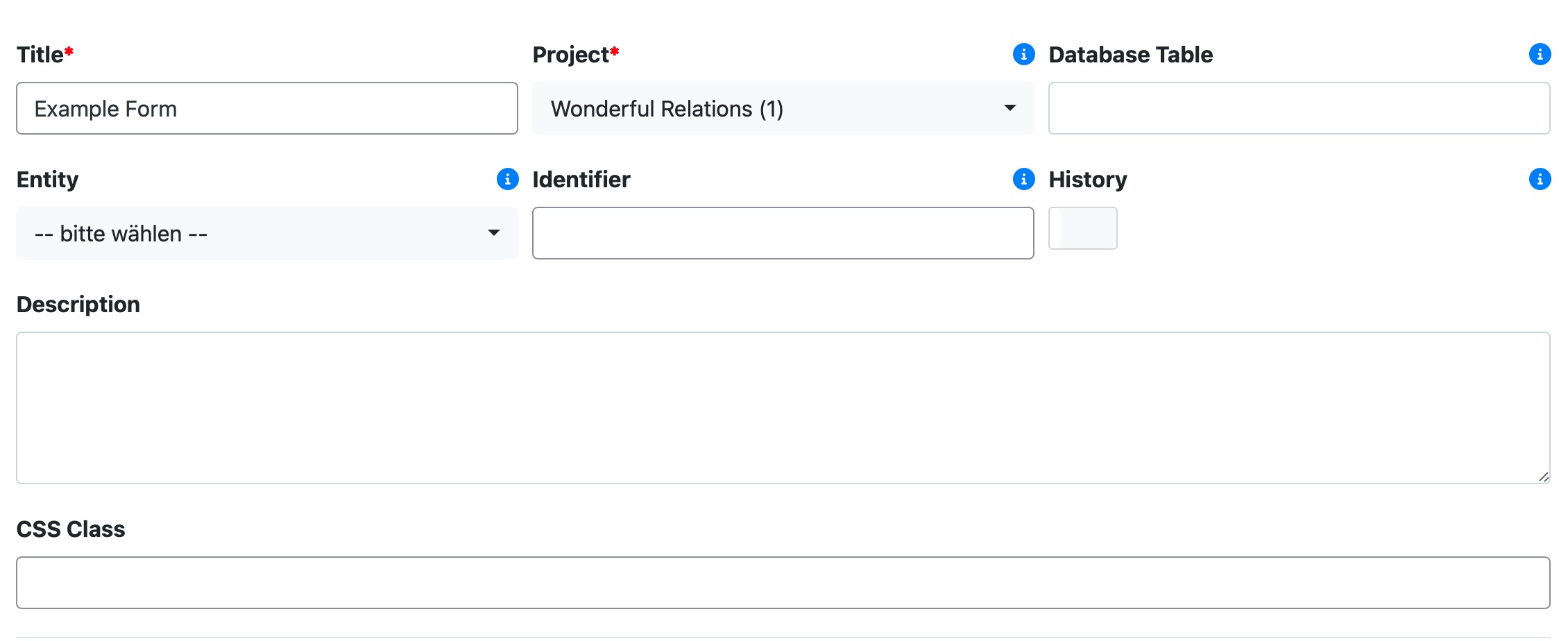
Title
Defines the name of the form, displayed in the UI.
Project
Associates the form with a specific Wonderful Relations Project.
Database Table
The database table where form data is stored. If it does not exist, it will be created automatically.
Entity
The entity that the form represents in the database.
Identifier
(Optional) A unique identifier for programmatic access.
History
Enables or disables history tracking for changes made within the form.
Description
A brief explanation of the form’s purpose.
CSS Class
Custom styling for the form layout using Bootstrap classes.
Components
Buttons
Standard buttons (Save, Save & Continue) Custom buttons for additional actions See Form Buttons
Fields
Various input types. See Form Fields
Linked Forms
Support for 1-n relationships, allowing subforms to be connected See Linked Forms
Tasks
Automated actions triggered before or after an event (e.g., on form save) See Tasks
Options
type
Option type: wp_optionsallows you to use the Option wp_option: your_wp_option in the Form Files.
Key: type Value: wp_options
Example Use Case: Creating a Settings Form for a Plugin Backend
Suppose you want to create a settings form for your plugin’s backend. Using Wonderful Relations Forms, you can easily define multiple configuration options without manually handling form storage.
A key advantage is the ability to store settings directly in WordPress options (wp_options).
So in example you add a toggle field to your form with the following option:
wp_option: your_project_enable_cron_jobs
Now, whenever a user enables or disables this setting, it is automatically stored in wp_options. You can access this value in your plugin code as follows:
if ( !get_option("your_project_enable_cron_jobs") ) {
// Option is not enabled
}Option type: external allows you to use the Action wr_form_external_save Form Files.
Key: type Value: external
Example Use Case: Allows handling form submissions via a WordPress action instead of storing data directly in the database.
See Actions wr_form_external_save
