Function: UNION
The UNION function in Wonderful Relations allows you to combine the results of multiple queries into a single unified result set—similar to how SQL UNION works. This is particularly useful when you want to aggregate data from different sources with matching structure.
Each query included in the union must return the same number of columns, with matching data types and order. This requirement ensures compatibility when merging rows across different query blocks.
Purpose
Use UNION when you want to:
- Combine logically related but structurally separated datasets
- Reuse existing queries to construct composite views
Parameters
Each UNION entry contains the following parameters:
Query
The referenced query to be included in the union.
Sort Order
Defines the order in which the union queries are applied.
Condition (Optional)
If set, the union query is wrapped and a WHERE clause is applied directly to its result set.
Example: Basic UNION
Combining two queries (Query B and Query C) in Query A:
SELECT * FROM (
QUERY_B
UNION
QUERY_C
) QUERY_AExample: UNION with Conditions
Each unioned query can also have its own condition:
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT * FROM (QUERY_B) WHERE CONDITION_B
UNION
SELECT * FROM (QUERY_C) WHERE CONDITION_C
) QUERY_AVisual Example:
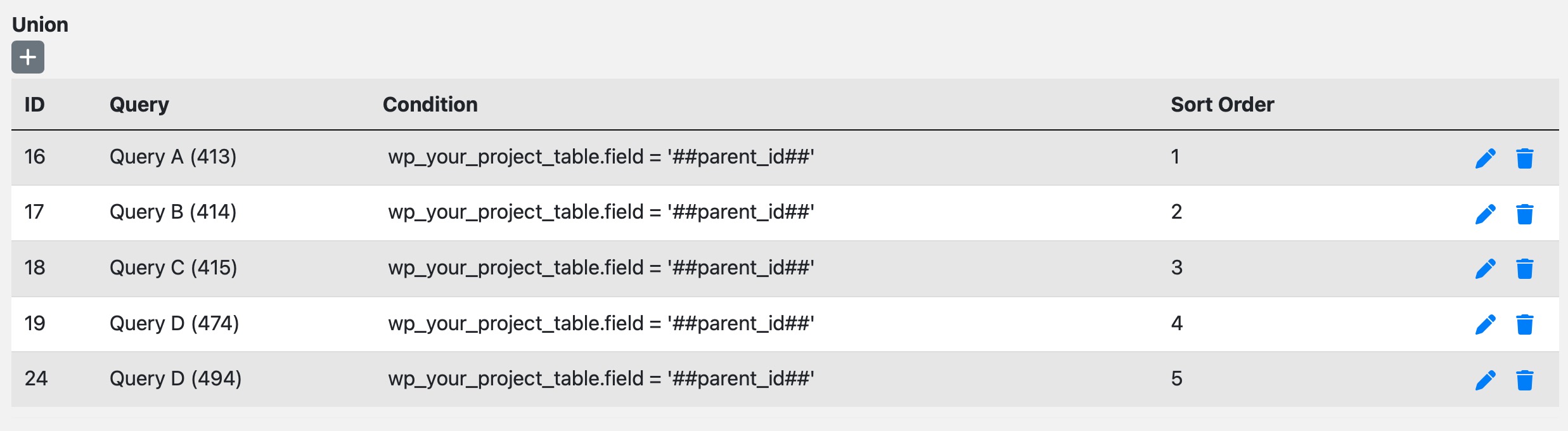
In Wonderful Relations, these conditions are defined in the union configuration and automatically applied during query execution.
Summary
✅ Combines multiple queries into one unified result set
✅ Supports individual filtering for each union component
✅ Preserves query reusability and modularity
The UNION function brings flexibility and composability to Wonderful Relations queries, empowering you to build powerful, multi-source views with ease.
